The Electric Revolution: Your Complete Guide to EVs and Sustainable Driving

Introduction: Electrifying the Road Ahead
The automotive landscape is undergoing a monumental shift, propelled by advancements in electric vehicles (EVs) and a growing global commitment to sustainable transport. For many, the idea of an eco-friendly car has transitioned from a futuristic concept to a tangible, accessible reality. This electric vehicle guide is your comprehensive resource to understanding the heart of this revolution: EVs. From unraveling the profound EV benefits for both your wallet and the planet, to demystifying electric car charging and electric car range, we’ll navigate the intricacies of EV technology that are reshaping the future of driving. Whether you’re considering buying an electric car, curious about EV ownership, or simply want to grasp the current EV market trends, prepare to embark on an enlightening journey into the world of sustainable mobility.
Understanding Electric Vehicles: More Than Just a Car
At its core, an electric vehicle is powered by one or more electric motors, using energy stored in rechargeable batteries. This contrasts sharply with traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles that rely on fossil fuels. But the distinction goes far beyond the powertrain. The silent acceleration and immediate torque often surprise first-time drivers, revealing a level of refinement rarely found in conventional cars.
The Different Types of EVs
Not all EVs are created equal. Understanding the various categories is crucial for any potential owner, as each offers a unique balance of range, performance, and charging flexibility:
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
These are what most people envision when they hear “electric car.” BEVs run solely on electricity, with no gasoline engine whatsoever. They produce zero tailpipe emissions, making them the purest form of eco-friendly cars. Popular electric car models like the Tesla Model 3, Nissan Leaf, and Chevrolet Bolt are prime examples of BEVs, showcasing diverse options for range and features.
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs)
PHEVs combine an electric motor and battery with a gasoline engine. They can operate on electric power alone for a certain range (typically 20-50 miles), after which the gasoline engine kicks in or assists. This offers the flexibility of electric driving for daily commutes and gasoline for longer trips, effectively mitigating electric car range anxiety for those transitioning from traditional vehicles. Examples include the Toyota Prius Prime and Chrysler Pacifica Hybrid, offering a bridge to full electrification.
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)
While not directly part of the electric revolution in the same way BEVs and PHEVs are, HEVs (like the original Toyota Prius) use an electric motor to assist a gasoline engine, primarily improving fuel efficiency. They cannot be plugged in and rely on regenerative braking to recharge their small batteries. They serve as an important step in improving fuel economy without requiring external charging infrastructure.
The Undeniable Benefits of EVs: Why Make the Switch?
The shift to electric vehicles isn’t just a trend; it’s a strategic move towards a more sustainable and economically sound future. The EV benefits are multifaceted, appealing to environmentalists, budget-conscious drivers, and tech enthusiasts alike. From reduced running costs to a superior driving experience, the advantages are increasingly clear.
Environmental Impact: A Breath of Fresh Air
One of the most compelling reasons to embrace EVs is their positive environmental footprint. Electric car emissions are zero at the tailpipe, significantly reducing local air pollution and contributing to cleaner cities. While the electricity used to charge an EV might come from various sources (including fossil fuels), the overall emissions, even considering power generation, are often lower than gasoline cars, especially as renewable energy sources become more prevalent. This direct link to electric vehicle sustainability is a major driver for many consumers and governments globally, pushing towards a greener planet.
 Embrace a cleaner future:
Embrace a cleaner future: Electric vehicles significantly reduce urban air pollution, contributing to healthier environments and a more sustainable planet.
Economic Advantages: Saving Money in the Long Run
Beyond environmental considerations, EV ownership offers substantial financial perks that can lead to significant long-term savings:
- Lower Fuel Costs: Electricity is generally cheaper per mile than gasoline, especially when charging at home during off-peak hours. The fluctuating price of gasoline makes the predictable cost of electricity even more appealing.
- Reduced Maintenance:
EVshave fewer moving parts than ICE cars (no oil changes, spark plugs, or complex transmissions), leading to lowerEV maintenancecosts and less frequent service appointments. This simplicity translates to fewer headaches and more time on the road. - Government Incentives: Many regions offer generous
government EV incentives, including federal tax credits, state rebates, and local perks like HOV lane access, makingbuying an electric carmore affordable. These incentives can significantly offset the initial purchase price. - Tax Benefits: Some areas provide tax exemptions or reduced registration fees for
eco-friendly cars, further enhancing their economic appeal.
Superior Driving Experience: Performance and Innovation
EV technology delivers a distinctly superior driving experience, combining exhilarating performance with unparalleled refinement:
- Instant Torque: Electric motors provide instant, smooth acceleration from a standstill, offering a quiet yet powerful ride that often surprises drivers used to the lag of gasoline engines.
- Quiet Operation: The absence of an internal combustion engine makes
EVsremarkably quiet, enhancing comfort and reducing noise pollution in urban environments. This serene cabin experience is a major draw. - Advanced Technology:
Electric car innovationsoften include cutting-edge infotainment systems, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), and over-the-air software updates, keeping your vehicle modern and continually improving. These smart features integrate seamlessly into daily life.
 Experience the cutting edge:
Experience the cutting edge: EV interiors are often defined by minimalist design, large digital displays, and seamless integration of smart technology for an intuitive and connected driving experience.
Demystifying EV Charging: Powering Your Electric Journey
One of the most common concerns for prospective EV owners is electric car charging. Understanding the options and infrastructure is key to a seamless EV ownership experience, dispelling myths about inconvenience and limited access.
Charging Levels: Speed and Convenience
There are three primary levels of electric car charging, each offering different speeds and suitable for various situations:
Level 1 Charging (120V AC)
This is the simplest form, using a standard household outlet. It’s slow, typically adding 2-5 miles of range per hour, making it suitable for overnight charging for low-mileage drivers or as a supplementary option for topping off. It requires no special equipment beyond what often comes with the car.
Level 2 Charging (240V AC)
The most common type of home EV charging, Level 2 requires a dedicated 240V circuit (like an electric dryer outlet) and a charging station (EVSE). It adds 20-30 miles of range per hour, fully charging most EVs overnight or in several hours. This is also prevalent in public EV charging stations at workplaces, shopping centers, and parking garages. For a truly sustainable smart home experience, integrating your home EV charging with energy-saving gadgets can optimize your electricity consumption and even utilize renewable energy sources. Learn more about making your home greener and more efficient at HyperDaily’s Sustainable Smart Home Guide.
DC Fast Charging (DCFC or Level 3)
DC Fast Chargers are the fastest option, found predominantly at public EV charging stations along highways and major travel routes. They can add 100-200+ miles of range in just 20-30 minutes, crucial for long-range EVs and road trips. Compatibility varies between EV models and charging networks (e.g., CCS, CHAdeMO, Tesla Supercharger), so it’s essential to check your vehicle’s specifications.
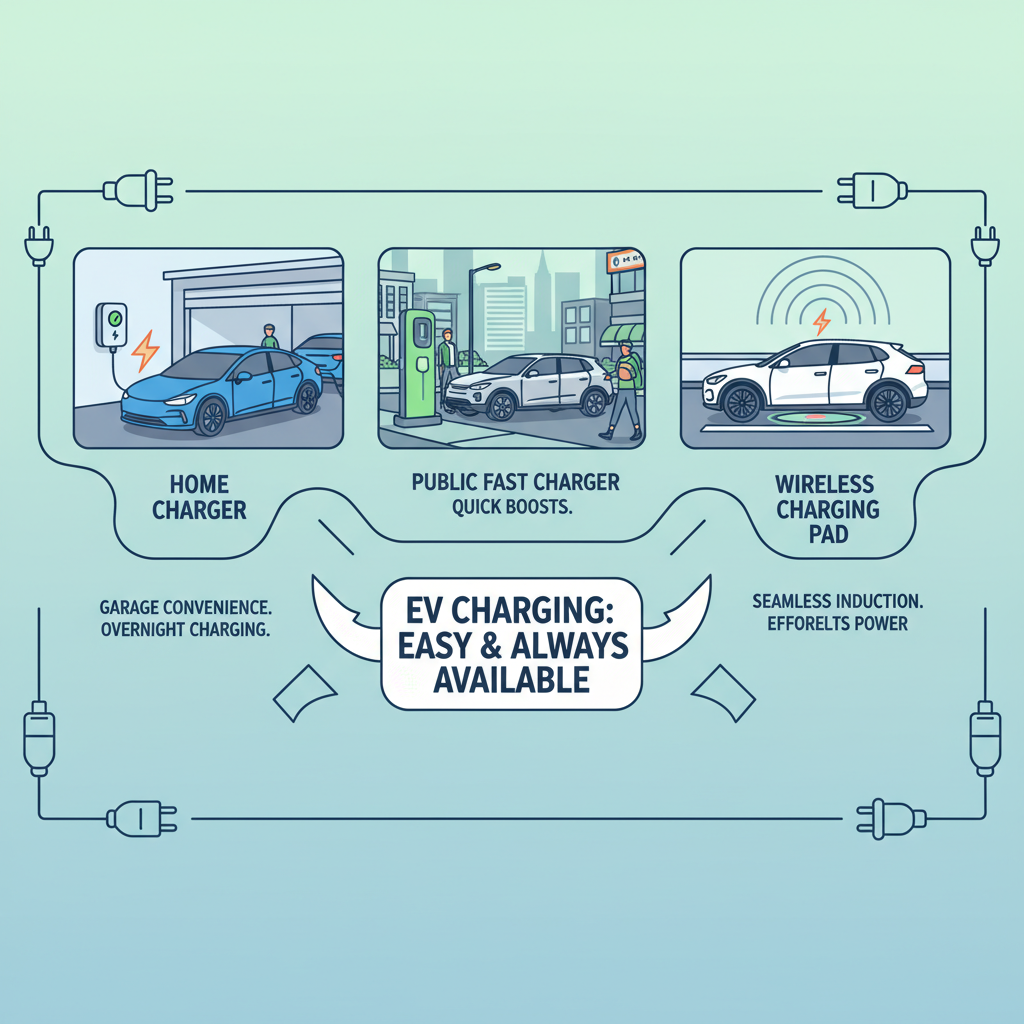 From home to highway:
From home to highway: Electric vehicle charging options span various speeds and locations, ensuring that powering up your EV is convenient and accessible, whether at home overnight or on the go with fast chargers.
The Evolving Electric Car Infrastructure
The electric car infrastructure is expanding rapidly, with significant investments from governments and private companies worldwide. Charging networks are growing, and the availability of public EV charging stations is constantly increasing. Charging apps and in-car navigation systems make finding available chargers easier than ever, alleviating electric car range anxiety and making long-range EVs a practical choice for extended travel and cross-country adventures. This robust infrastructure is a cornerstone of the future of driving.
EV Technology and Performance: Beyond the Battery
EV technology is a fascinating realm of engineering prowess, constantly pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in automotive design and performance. It encompasses not just the battery and motor, but also sophisticated energy management systems and innovative design.
Electric Car Range and Battery Life
Electric car range is a critical factor for many buyers, and it has improved dramatically in recent years. Modern EVs offer impressive ranges, with many long-range EVs exceeding 300 miles on a single charge. Factors influencing range include battery size, vehicle efficiency, aerodynamic design, driving style, and external temperature.
EV battery life is another frequent question, often accompanied by misconceptions. Most EV batteries are designed to last the lifetime of the vehicle, typically guaranteed for 8 years or 100,000 miles. Battery degradation does occur over time, but it’s often gradual and less significant than many perceive, with many batteries retaining over 80% of their capacity after extensive use. Advanced battery management systems help maintain optimal performance and longevity.
Electric Car Innovations: The Future is Now
The pace of electric car innovations is breathtaking, promising even more efficient, powerful, and convenient EVs in the near future. We’re seeing groundbreaking developments such as:
- Solid-State Batteries: Promising higher energy density, faster charging, greater safety, and potentially longer
EV battery lifecompared to current lithium-ion technology. - Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology: Enabling
EVsto send stored energy back to the grid during peak demand, turning them into mobile power banks and integrating them into smart energy ecosystems. - Enhanced Connectivity and Autonomy:
EVsare often at the forefront of connected car features and autonomous driving capabilities, integrating seamlessly with digital ecosystems and offering advanced safety features. This focus on advanced tech can be seen across various sectors, including how AI is shaping our daily productivity. Discover more about unlocking potential with top AI tools for everyday productivity. - Performance EVs:
Luxury EVsand high-performanceelectric car modelsare demonstrating that electric powertrains can deliver blistering acceleration and exhilarating driving dynamics that rival or surpass their gasoline counterparts, redefining what performance means.
Electric Car vs. Gasoline Car: A Head-to-Head Comparison
When considering buying an electric car, a direct comparison with traditional gasoline cars is inevitable. Understanding the fundamental differences helps clarify the advantages and disadvantages of each.
| Feature | Electric Cars (EVs) | Gasoline Cars |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Source | Electricity (rechargeable battery) | Gasoline/Diesel (internal combustion engine) |
| Emissions | Zero tailpipe emissions, lower overall carbon footprint | Significant tailpipe emissions (CO2, NOx, particulates), higher overall carbon footprint |
| Running Costs | Generally lower (cheaper electricity, simpler EV maintenance) | Higher (volatile fuel prices, more frequent and complex maintenance) |
| Performance | Instant torque, smooth, quiet acceleration, often quicker 0-60 mph | Varying performance, engine noise, vibrations, powerband limitations |
| Maintenance | Simpler, fewer fluids, fewer moving parts (no oil changes, spark plugs, etc.) | Regular oil changes, spark plugs, belts, complex engine/transmission repairs |
| Refueling Time | Minutes (fast charging) to hours (home charging); can vary based on level | Minutes (quick and widely available) |
| Environmental Impact | Significantly lower overall impact, especially with renewable energy grids | Higher impact through resource extraction, combustion, and emissions |
| Incentives | Often eligible for government EV incentives, tax credits, and other perks | Rarely eligible for specific environmental incentives |
The EV Market: Trends, Models, and Ownership
The EV market trends indicate robust growth and diversification, offering a wide array of electric car models to suit every need and budget. This expanding market means more choices and increasing accessibility for consumers.
Current EV Market Trends
The global EV market is experiencing unprecedented expansion, driven by a confluence of factors:
- Increased Consumer Demand: Growing environmental awareness, rising fuel prices, and a desire for advanced technology are fueling consumer interest in
electric vehicles. - Government Regulations: Stricter emissions standards, mandates for EV adoption, and investment in
electric car infrastructureare pushing manufacturers to accelerate theirEVofferings. - Technological Advancements: Longer ranges, faster charging, and more affordable batteries are making
EVsmore practical and appealing than ever before. - Diverse Offerings: A proliferation of
electric car modelsfrom virtually every major automaker, including SUVs, trucks, and sedans, ensures that there’s anEVfor every lifestyle and requirement.
Top Electric Car Models: From Affordable to Luxury
The market now caters to a broad spectrum of buyers, demonstrating the versatility and appeal of EV technology:
Affordable EVs
For those seeking accessible sustainable transport, affordable EVs like the Nissan Leaf, Chevrolet Bolt EUV, and Hyundai Kona Electric offer excellent value, respectable range, and practical features for daily commuting and city driving. These models are breaking down barriers to entry for EV ownership.
Luxury EVs
The luxury EVs segment boasts impressive engineering, opulent interiors, and cutting-edge performance. Models like the Tesla Model S, Porsche Taycan, Lucid Air, and Mercedes-Benz EQS redefine premium driving with electrifying acceleration, advanced features, and unparalleled comfort.
EVs for Every Lifestyle
Beyond sedans, the market has seen an explosion of electric SUVs (Ford Mustang Mach-E, Hyundai Ioniq 5, Kia EV6) and even electric pickup trucks (Ford F-150 Lightning, Rivian R1T), proving that EVs are versatile enough for any adventure or utility need. For those who love to travel green, these diverse options make eco-friendly adventures more accessible than ever. Explore guides to sustainable and eco-friendly adventures.
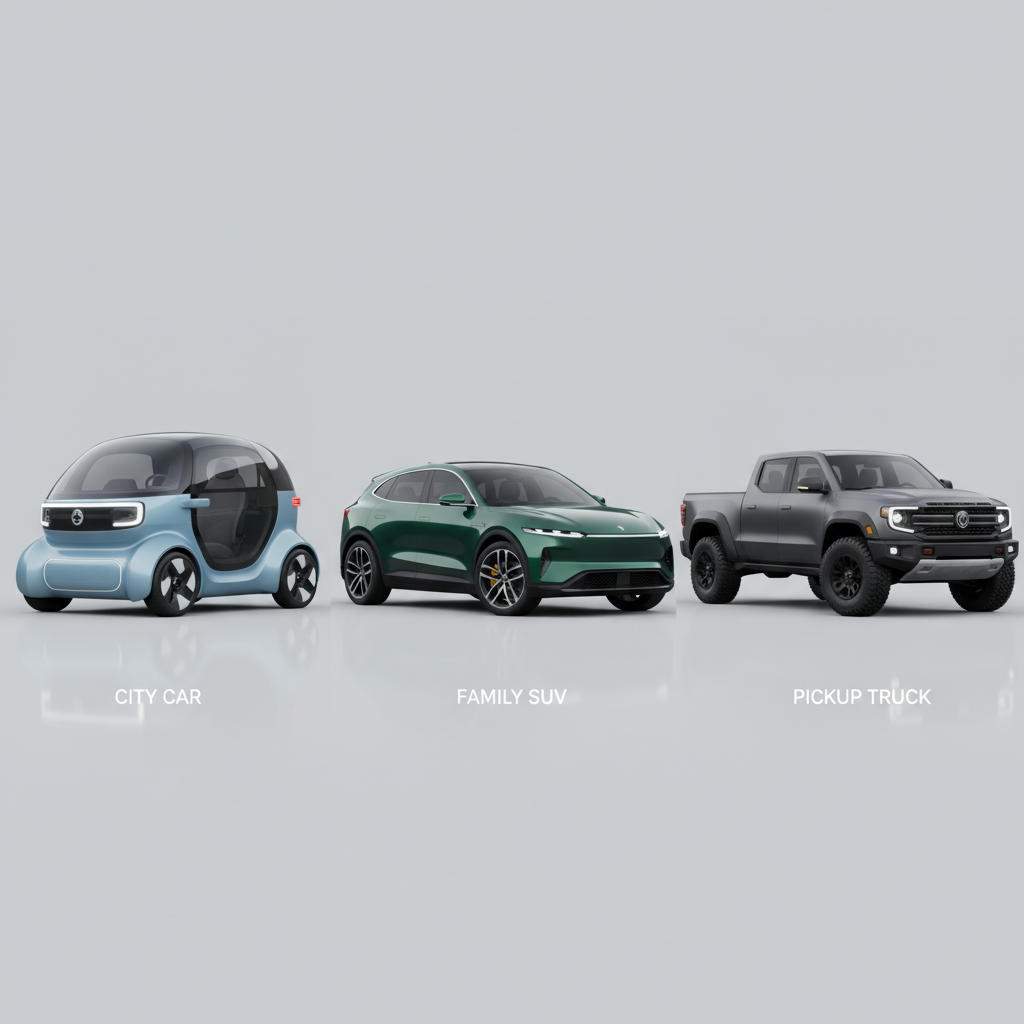 A diverse fleet:
A diverse fleet: Electric vehicle models now encompass everything from compact city cars to robust SUVs and powerful pickup trucks, offering a sustainable option for every lifestyle and need.
Buying an Electric Car: What to Consider
Buying an electric car involves several key considerations to ensure you choose the right vehicle for your needs and lifestyle:
- Budget & Incentives: Factor in the upfront purchase price, available
government EV incentives, potential federal and state tax credits, and long-term running costs to get a complete financial picture. - Range Needs: Carefully evaluate your daily driving habits, commuting distances, and typical road trip frequencies to choose an
EVwith sufficientelectric car range.Long-range EVsare ideal for frequent highway driving. - Charging Access: Assess your
home EV chargingoptions (do you have a garage or dedicated parking?) and the availability ofpublic EV chargingin your area, including workplaces and frequent destinations. - EV Reviews: Consult
EV reviewsfrom reputable automotive journalists and consumer organizations to compare performance, features, reliability, and real-world range of differentelectric car models. - Pros and Cons: Weigh the
electric car pros and conscarefully, considering factors like charging time, initial cost, and environmental impact, to ensure it aligns with your lifestyle and expectations.
EV Ownership: Pros, Cons, and Maintenance
Understanding the full scope of EV ownership means looking at both the advantages and potential drawbacks, as well as the unique aspects of EV maintenance that set it apart from traditional vehicles.
Electric Car Pros and Cons: A Balanced View
Like any significant purchase, EV ownership comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. A balanced perspective is crucial for making an informed decision.
Pros:
- Environmental Benefits: Zero tailpipe emissions, significantly reduced carbon footprint, contributing to cleaner air and a healthier planet. This is a core aspect of
electric vehicle sustainability. - Lower Running Costs: Cheaper “fuel” (electricity), reduced
EV maintenanceneeds due to fewer moving parts, and potentialgovernment EV incentiveslead to substantial long-term savings. - Quiet and Smooth Ride: The electric powertrain provides a remarkably quiet, refined, and smooth driving experience, free from engine vibrations.
- Performance: Instant torque and quick acceleration offer an exhilarating and responsive driving dynamic that many find superior to gasoline cars.
- Technological Advancement:
EVsare often pioneers of cutting-edge features, including advanced infotainment, driver-assistance systems, and over-the-air updates. - Government Incentives: Financial benefits and perks, such as tax credits, rebates, and preferential parking, can make
EVsmore attractive.
Cons:
- Higher Upfront Cost:
Electric vehiclescan often be more expensive to purchase than comparable gasoline cars, although the emergence ofaffordable EVsis narrowing this gap. - Charging Time: While DC fast charging is quick, fully charging an
EVat home can take several hours, which is longer than a typical gas station stop. - Range Anxiety (diminishing): The concern about running out of charge before reaching a charging station, though
electric car rangeis improving dramatically andelectric car infrastructureis expanding. - Charging Infrastructure Gaps: While expanding rapidly,
public EV chargingcan still be less ubiquitous than gas stations in some remote areas, requiring more planning for long trips. - Battery Replacement Cost: Potentially high if needed outside warranty (though rare, and
EV battery lifeis generally long).
EV Maintenance: Simpler, Smarter
EV maintenance is generally simpler and less frequent than for gasoline cars, contributing to lower ownership costs and less hassle. Key differences include:
- No Oil Changes: Electric motors don’t use engine oil, eliminating one of the most common and recurring maintenance tasks for gasoline vehicles.
- Fewer Moving Parts: No spark plugs, timing belts, exhaust systems, or complex transmissions mean fewer components to wear out or break down.
- Brake Longevity: Regenerative braking, which uses the electric motor to slow the car and recapture energy, significantly reduces wear and tear on physical brake pads, leading to longer brake life.
- Regular Checks: Tires (rotation and pressure), brakes (pads still need occasional checks), wiper fluid, and cabin air filters are still standard maintenance items, similar to any vehicle.
- Battery Health: Sophisticated software diagnostics continuously monitor
EV battery lifeand health, alerting owners to any potential issues.
The simplified maintenance contributes to lower long-term EV ownership costs, making electric vehicles an increasingly attractive proposition.
The Future of Driving: Electric Vehicle Sustainability and Innovation
The future of driving is undeniably electric. The trajectory of electric vehicle sustainability and electric car innovations points towards a world where transportation is cleaner, smarter, and more integrated into a broader sustainable ecosystem.
Driving Towards a Sustainable Future
The overarching goal of the electric revolution is to achieve true sustainable transport. As electricity grids become greener with increasing reliance on renewable energy sources, the lifecycle emissions of electric vehicles will continue to decrease, solidifying their role as the cornerstone of eco-friendly cars. This holistic approach to sustainability extends beyond just transportation; it’s about conscious choices in every aspect of life, from how we travel to what we wear and how we power our homes. Dive into exploring sustainable style and eco-friendly fashion choices for a complete sustainable lifestyle, or learn more about sustainable smart home solutions.
Emerging Innovations in EVs
Looking ahead, we can expect further groundbreaking electric car innovations that will redefine our relationship with personal mobility:
- Wireless Charging: Convenient, hands-free charging without cables, allowing for effortless power transfer at home or in public parking spaces.
- Hyper-Efficient Motors: Development of even greater efficiency and power from smaller, lighter electric motors, maximizing
electric car rangeand performance. - Autonomous Electric Fleets:
EVsare ideal platforms for self-driving technology, paving the way for autonomous ride-sharing and delivery services that could revolutionize urban mobility and logistics. - Improved Battery Recycling: Enhanced and more efficient methods for recycling
EV battery lifecomponents, reducing waste and the demand for raw materials, further boostingelectric vehicle sustainability.
The continuous stream of electric car innovations ensures that EVs will remain at the forefront of technological advancement, constantly redefining our relationship with personal mobility and pushing us towards a more sustainable transport future.
Conclusion: Embrace the Electric Revolution
The electric revolution is here, transforming how we commute, travel, and interact with our environment. This complete guide to EVs has illuminated the myriad EV benefits, from their profound impact on electric vehicle sustainability and reduced electric car emissions to their economic advantages and superior driving dynamics. We’ve explored EV technology, demystified electric car charging and electric car range, and navigated the exciting landscape of electric car models and EV market trends.
While buying an electric car presents unique considerations, the electric car pros and cons heavily favor the former for those committed to the future of driving. With expanding electric car infrastructure, robust government EV incentives, and continuous electric car innovations, EV ownership is becoming more appealing and accessible than ever before. It’s not just about a mode of transport; it’s about making a conscious choice for a cleaner, quieter, and more efficient world.
Are you ready to be part of the change? Explore the exciting world of electric vehicles and drive towards a sustainable tomorrow. For more insights into how technology is shaping our world, including creative fields and generative AI, visit HyperDaily and explore more articles on HyperDaily Blog.
FAQs
Q1. What are the primary benefits of owning an electric vehicle?
The primary EV benefits include significantly reduced running costs due to cheaper electricity and lower EV maintenance, zero tailpipe electric car emissions contributing to cleaner air, a quieter and smoother driving experience, and eligibility for government EV incentives.
Q2. How long does it take to charge an electric car?
Electric car charging times vary widely depending on the charging level and the EV’s battery size. Level 1 (standard outlet) can take 20+ hours for a full charge. Level 2 (240V home or public charger) typically takes 4-10 hours. DC Fast Charging can provide 80% charge in 20-60 minutes, making long-range EVs practical for road trips.
Q3. What is the typical range of an electric car?
The electric car range varies significantly by electric car model and battery size. Many modern EVs offer between 200-300 miles on a single charge, with some long-range EVs exceeding 400 miles. Factors like driving style, speed, and climate control usage can affect actual range.
Q4. Are electric cars truly eco-friendly considering battery production and electricity source?
While battery production has an environmental footprint, electric car emissions are zero at the tailpipe. When considering the entire lifecycle, EVs generally have a lower carbon footprint than gasoline cars, especially as electricity grids increasingly rely on renewable energy sources. Electric vehicle sustainability is an ongoing focus for continuous improvement.
Q5. What kind of maintenance do electric vehicles require?
EV maintenance is generally simpler and less frequent than gasoline cars. They don’t require oil changes, spark plug replacements, or complex transmission services. Routine maintenance typically includes tire rotations, brake inspections (less wear due to regenerative braking), fluid checks (wiper fluid), and cabin air filter replacements.
Q6. Are government incentives available for buying an electric car?
Yes, many governments and local authorities offer government EV incentives to encourage buying an electric car. These can include federal tax credits, state rebates, reduced sales tax, HOV lane access, and other perks, significantly reducing the effective purchase price of electric vehicles.
Q7. How does the cost of charging an EV compare to fueling a gasoline car?
Typically, the cost of electric car charging (electricity) is lower per mile than the cost of gasoline. This can lead to substantial savings over the lifetime of EV ownership, especially when utilizing home EV charging during off-peak electricity hours.
Q8. What is “range anxiety” and is it still a major concern for EV owners?
Range anxiety refers to the fear of an EV running out of battery power before reaching a charging station. While it was a significant concern in early EVs, advancements in electric car range (many now exceed 250+ miles) and the rapid expansion of electric car infrastructure (more public EV charging stations) have greatly diminished this concern for most EV ownership scenarios.